- Profil
- Departemen & Staf
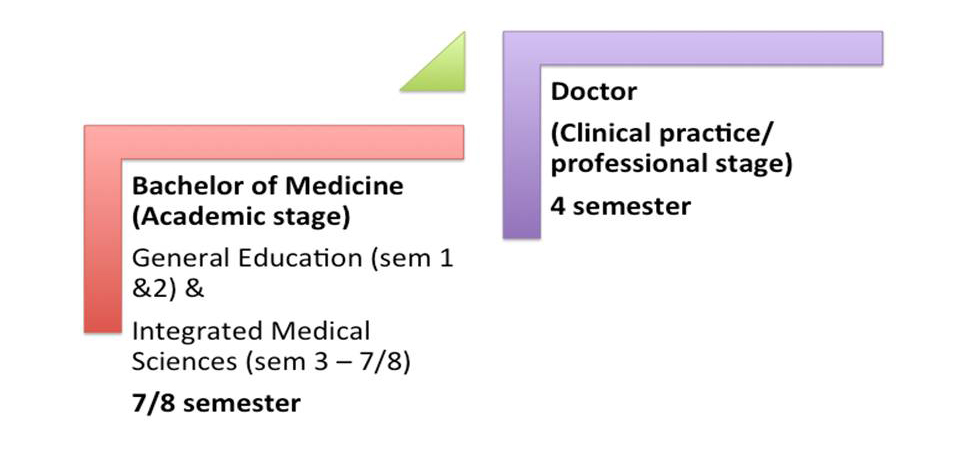
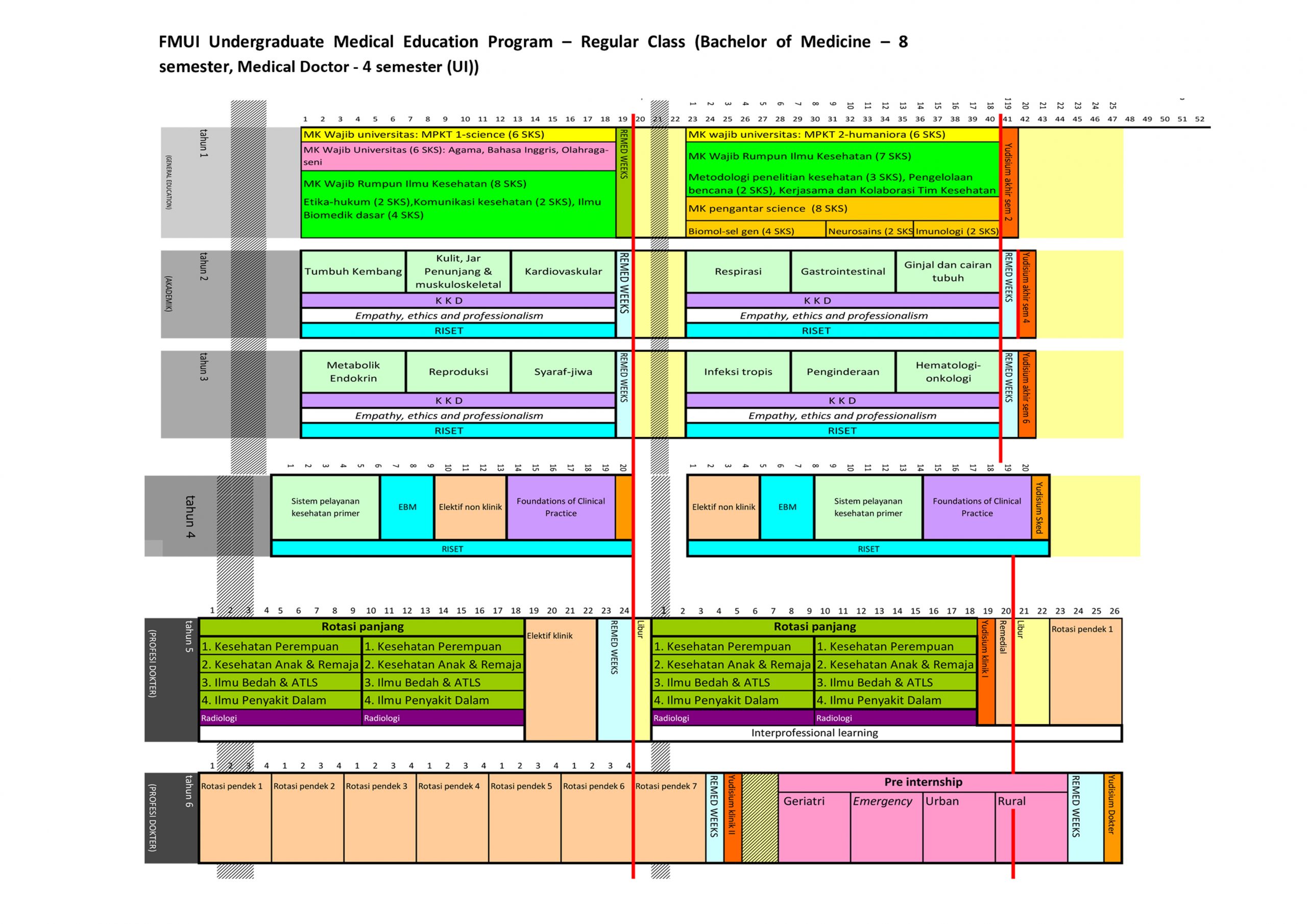
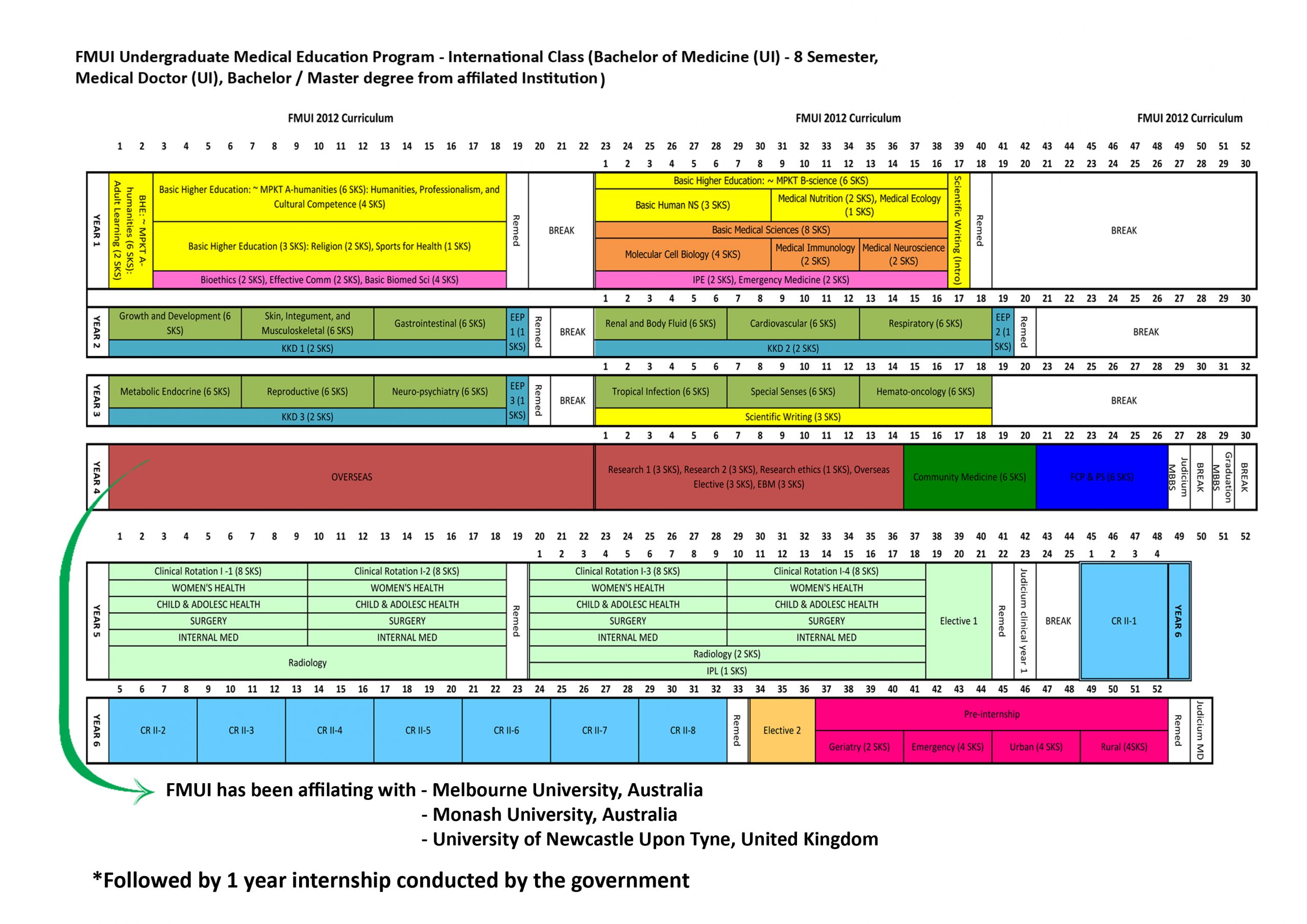
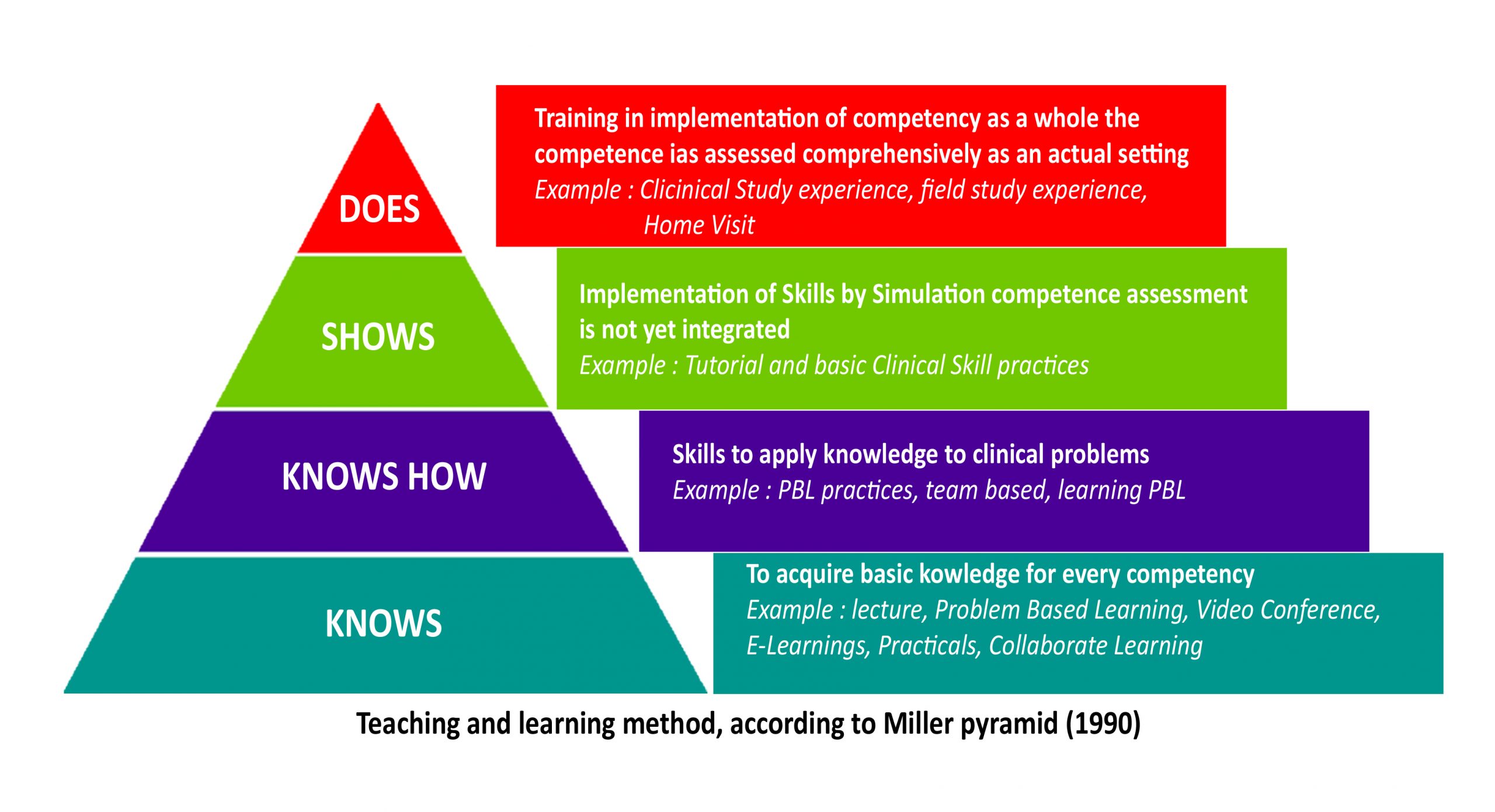
- Pre Klinik
- Klinik
- Anestesiologi dan Intensive Care
- Dermatologi dan Venereologi
- Gigi dan Mulut
- Ilmu Bedah
- Ilmu Bedah Saraf
- Ilmu Gizi
- Ilmu Kesehatan Jiwa
- Ilmu Kedokteran Forensik dan Medikolegal
- Ilmu Kesehatan Anak
- Ilmu Kesehatan Mata
- Telinga Hidung Tenggorok (THT) KL
- Ilmu Penyakit Dalam
- Kardiologi dan Kedokteran Vaskular
- Mikrobiologi
- Neurologi
- Obstetri dan Ginekologi
- Orthopaedi dan Traumatologi
- Patologi Klinik
- Pulmonologi dan Kedokteran Respirasi
- Radiologi
- Urologi
- Profil Guru Besar
- Profil Staf
- Pendidikan
- Riset & Publikasi
- Ventura & Kerja Sama
- Kuliah di FKUI