A process in place to treat wastewater.
Faculty of Medicine has installed the domestic wastewater treatment plant or IPAL (Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah) to recycle water. The recycled water is streamed to infiltration wells, which then can be used as reserved water resources. The capacity is 30 m3/hour with water sourced from Sewage Treatment Plant with a capacity of 11 m3/hour. The recycled water is utilized to flush toilets.
[6.3.2] Preventing Water System Pollution
Processes to prevent polluted water entering the water system, including pollution caused by accidents and incidents at the university.
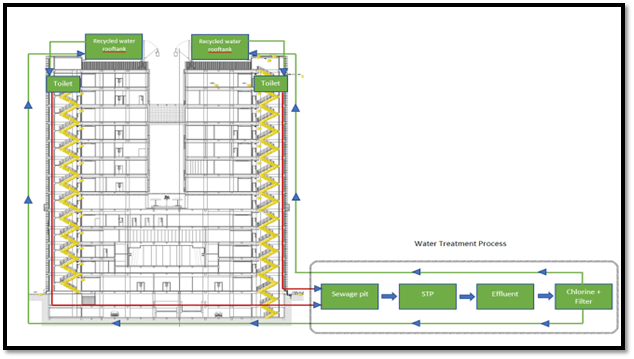
Wastewater at the Faculty of Medicine comprises household waste, used AC water, laboratory waste, and ablution water waste. Household waste includes water used for domestic purposes, such as from sinks, cafeteria waste, and urinals, as well as leftover ablution water. The treatment of household waste is carried out through a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP), which functions to collect effluent from household sources. This liquid waste undergoes processing in a contact tank, ultimately serving as a source of recycled water. It is then further treated at the Water Treatment Plant (WTP). The managed output from the WTP is stored in a Ground Water Tank (GWT) and pumped to the roof for subsequent use in flushing toilets.
[6.3.3] Free Drinking Water Provided
Provide free drinking water for students, staff and visitors (e.g. drinking water fountains).
FMUI provides free drinking water for faculty members and students, with strategically placed water dispensers in various accessible areas, including FMUI Building H, the upper lobby, the staff office, and the clinical students’ dining room.
The aim of utilizing recycled water is to reduce water consumption and maintain water quality. This involves conserving water throughout the life of the building by managing rainwater runoff and recycling used water for reuse, such as refilling toilet tanks or watering plants.
1. Percentage of Recycled Water:
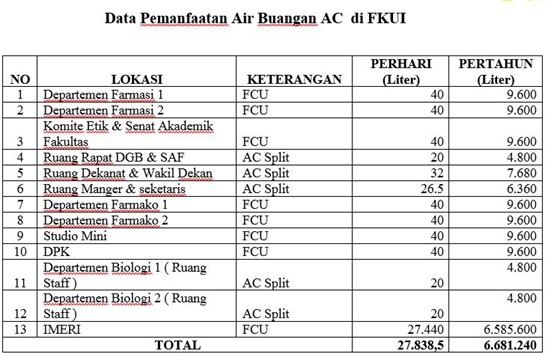
The utilization of drainage water from air conditioning systems is done by connecting the AC drainpipes to a storage container (drum). Within 6 to 8 hours, each 20-liter drum will be filled with AC wastewater. Once a drum is full, it will be moved (during the dry season, it will be transferred to the rainwater storage) and replaced with an empty drum by cleaning staff and security personnel (outside of operational hours).

2. Water utilization Diagram (Diagram Pemanfaatan Air)
3. Diagram Pengolahan Air Gedung IMERI (Grey dan Black Water)

Sumber Air:
- PDAM water enters the groundwater tank, is pumped up to the roof water tank in each tower and is distributed to all floors. It supplies toilets, pantries, wash basins, urinals, jet showers, and sinks in the laboratories. The wastewater is then sent to the STP/WTP for treatment before being used for toilet flushing.
- Rainwater + AC drainage water → infiltration wells.

4. Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) dan Water Treatment Plant (WTP)
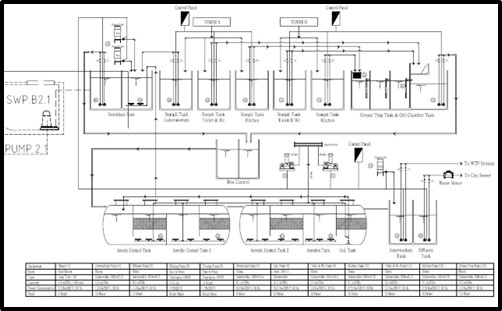
5. Recycled Water Storage in the IMERI Building

6. Process of Maintaining STP/WTP
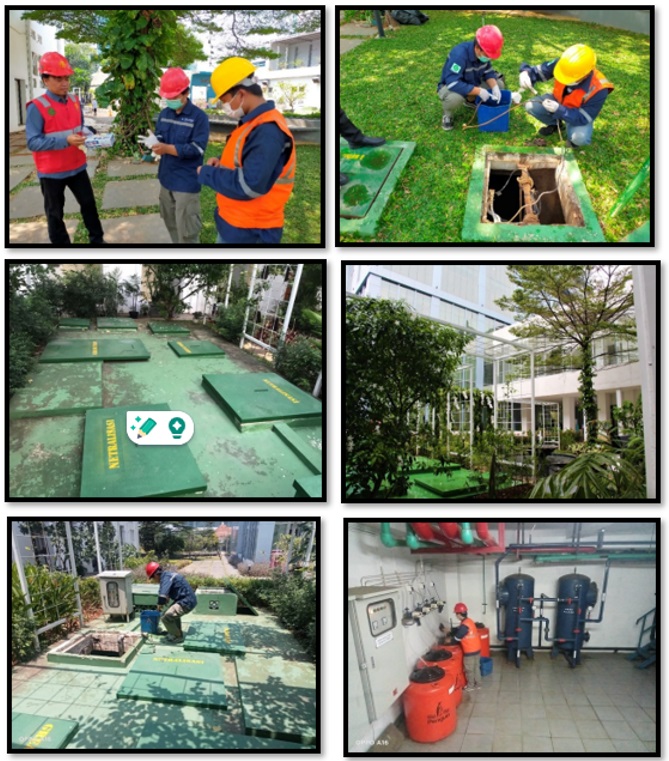

7. Adding chlorine powder for clean recycled water

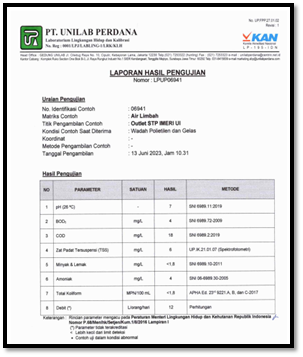
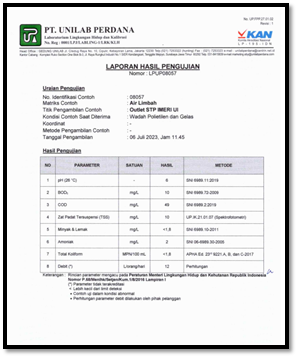
8. Results of Wastewater Quality Standard Testing Analysis (Uji Baku Mutu Air Limbah)
The following example shows that during the periods of June and July 2023, the test results indicate compliance with national wastewater quality standards for effluent discharged from the wastewater treatment plant (IPAL). The analysis of the IPAL effluent shows that all parameters are below the threshold limits, confirming that the quality of the STP effluent meets the required standards.
WATER FOUNTAIN SYSTEM AND WATER QUALITY MONITORING

ISO CERTIFICATE FOR FKUI LABORATORY (INCLUDING ASSESSMENT ON WATER CONSERVATION AND POLLUTION CONTROL)


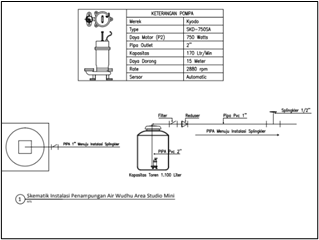
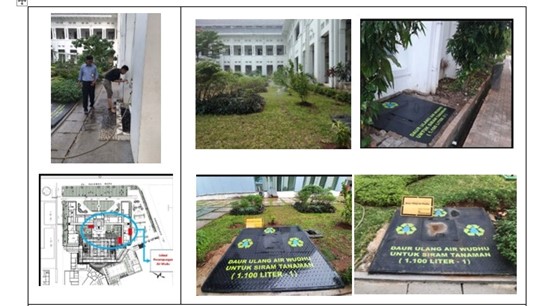
9. Utilization of Used Ablution Water (Air Wudhu)
Another use of recycled water is the repurposing of used ablution water to irrigate plants, totaling 3 units (each 1,100 liters).
SCHEME FOR USED ABLUTION WATER (AIR WUDHU) RECYCLING

AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION PROCESS AND LOCATION OF USED ABLUTION (WUDHU) WATER STORAGE
10 Utilization of Rainwater Runoff
The utilization of rainwater runoff (as part of the water conservation program) is being implemented in phases by connecting rainwater drainage pipes to underground storage tanks. Currently, 25% of the rainwater runoff from Building H at FKUI has been redirected to storage for reuse in irrigating plants, while 75% is directed to ponds and infiltration wells to return to the ground.

11. Regular Maintenance of the PDAM System by PDAM Personnel
Recycled water is a regular source of water used on the campus of the Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, with the quality of the produced water having been tested for suitability. The Water Treatment Plant managing this recycled water has a capacity of 30 m³/hour, sourced from the Sewage Treatment Plant with a capacity of 11 m³/hour. The recycled water is obtained from wastewater sources at FKUI. The liquid waste at FKUI consists of two types:
- Household Waste.
- Ablution Wastewater and Rainwater Runoff: A system has been developed for collecting ablution water and rainwater runoff for recycling, which can be used for automatic irrigation of plants at FKUI.
- Laboratory Waste.
12. Household waste management at FKUI is handled through the Sewage Treatment Plant (STP), which collects waste from toilets and sinks (kitchens). This liquid waste is processed in a contact tank and subsequently becomes a source of recycled water (which is then treated in the Water Treatment Plant). In the WTP, the water is stored in the Ground Water Tank (GWT) and pumped to the roof for use in toilet flushing.
Laboratory waste consists of two types: physical and non-physical (liquid), with management as follows:
- Physical Waste: Units/clusters/departments collect laboratory waste in designated special bins, which are then disposed of in a temporary storage facility specifically for laboratory waste. The transport of this laboratory waste is carried out by a certified third party.
- Non-Physical Waste (Liquid) consists of two types:
- Chemical Laboratory Waste: Units/clusters/departments collect liquid laboratory waste in designated special bins, which are then disposed of in a temporary storage facility specifically for liquid waste. The transport of this liquid laboratory waste is conducted by a certified third party.
- Washwater Waste: This liquid waste is processed in a contact tank, which will later serve as a source of recycled water (subsequently treated in the Water Treatment Plant) and is stored in a separate tank.
Description:
- Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1569/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Kebijakan Mitigasi dan Adaptasi Perubahan Iklim Global di Fakultas Kedokteran UI.
- Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1570/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Kebijakan green building (Gedung Hijau) yang tercermin dalam pengembangan dan renovasi ruangan di FKUI.
- Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1573/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Tim Pengelolaan Air Bersih di Fakultas Kedokteran UI.
- Standar Operasional Prosedur Tentang Pemanfaatan Air Buangan AC (Air Conditioner) Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia, Tahun 2023.
All policy data can be accessed at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1-Y4ZjABv_SpuqwSNFoVFdMP--wbC-OMm
1. Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1569/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Kebijakan Mitigasi dan Adaptasi Perubahan Iklim Global di Fakultas Kedokteran UI


2. Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1570/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Kebijakan green building (Gedung Hijau) yang tercermin dalam pengembangan dan renovasi ruangan di Fakultas Kedokteran UI.


3. Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1573/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Tim Pengelolaan Air Bersih di Fakultas Kedokteran UI.


4. Standar Operasional Prosedur Tentang Pemanfaatan Air Buangan AC (Air Conditioner) Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia
[6.3.3] Free drinking water provided
FMUI provides free drinking water for faculty members and students, with strategically placed water dispensers in various accessible areas, including FMUI Building H, the upper lobby, the staff office, and the clinical students’ dining room.
[6.3.4] Water-conscious building standards
FMUI is implementing water-conscious building includes :
1. Recycle domestic wastewater by IPAL (Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah).
2. Installation of water-saving reminder stickers at ablution areas and sinks across FKUI premises.
3. Regular maintenance of existing STP/WTP, infiltration wells, and retention ponds.
4. Routine maintenance of the Groundwater Tank (GWT).
5. Continuous addition of new infiltration wells.
6. Expansion of Green Open Space at the Parasitology Department.
7. Plans for 2023 include the establishment of a Communal Green Open Space, addition of infiltration wells for rainwater runoff in the Salemba 4,6 area, and PGT Campus 16.
8. Improvement of flood control channels at Microbiology Building/IKK FMUI..
9. Installation of automatic timers for plant watering faucets.
10.List of Infiltration Wells at FKUI:
- Garden Area: 39.25 m3
- Parking Area (Diponegoro Street side): 43.175 m3
- IMERI Building Area: 160 m3
- Anatomy Area: 18 m3 using sigma tank material.
11. Retention Ponds:
- Garden Area: 235.2 m3
- IMERI Building Area: 117.6 m3
- Groundwater Tank located in the IMERI Building Area consists of 3 compartments: Groundwater Tank (Clean Water), Groundwater Tank (Hydrant), Groundwater Tank (Recycle).
12.Formation of a Water Management Team at FMUI




Surat Keputusan Dekan Nomor: SK 1573/UN2.F1.D/HKP.02.04/2022 tentang Tim Pengelolaan Air Bersih di Fakultas Kedokteran UI



































